Could America survive an electromagnetic attack (EMP)?
Click to read the full story: Could America survive an electromagnetic attack (EMP)?
While many of us have seen Hollywood’s version of an electromagnetic pulse attack (EMP) in films like “Broken Arrow,” but just how real do you expect that to be? In that film, John Travolta got to be over the top, and his destruction took out everything in the vicinity.
When much of Venezuela was plunged into darkness after a massive blackout last week, President Nicolás Maduro blamed the power outage on an “electromagnetic attack” carried out by the U.S.
The claim was met with skepticism. Blackouts are a regrettably frequent part of life in Venezuela, where the electric grid has fallen into serious disrepair. And Maduro’s administration provided no evidence of an electromagnetic attack.
This didn’t stop many Americans from wondering just what would happen if this happened to the United States. Would people be able to survive it and just how much damage does and EMP do to the human body?
“In Venezuela, it’s a lot easier for him to say we did something to him than he did it to himself,” said Sharon Burke, senior adviser at New America, a nonpartisan think tank, and former assistant secretary of defense for operational energy at the Department of Defense. “Their grid, it’s decrepit. It’s been in very poor shape. They’ve been starving their infrastructure for years.”
Nevertheless, Maduro’s claim has raised questions over what exactly is an electromagnetic attack, how likely is it to occur and what impact could it have.
WHAT IS AN ELECTROMAGNETIC ATTACK?
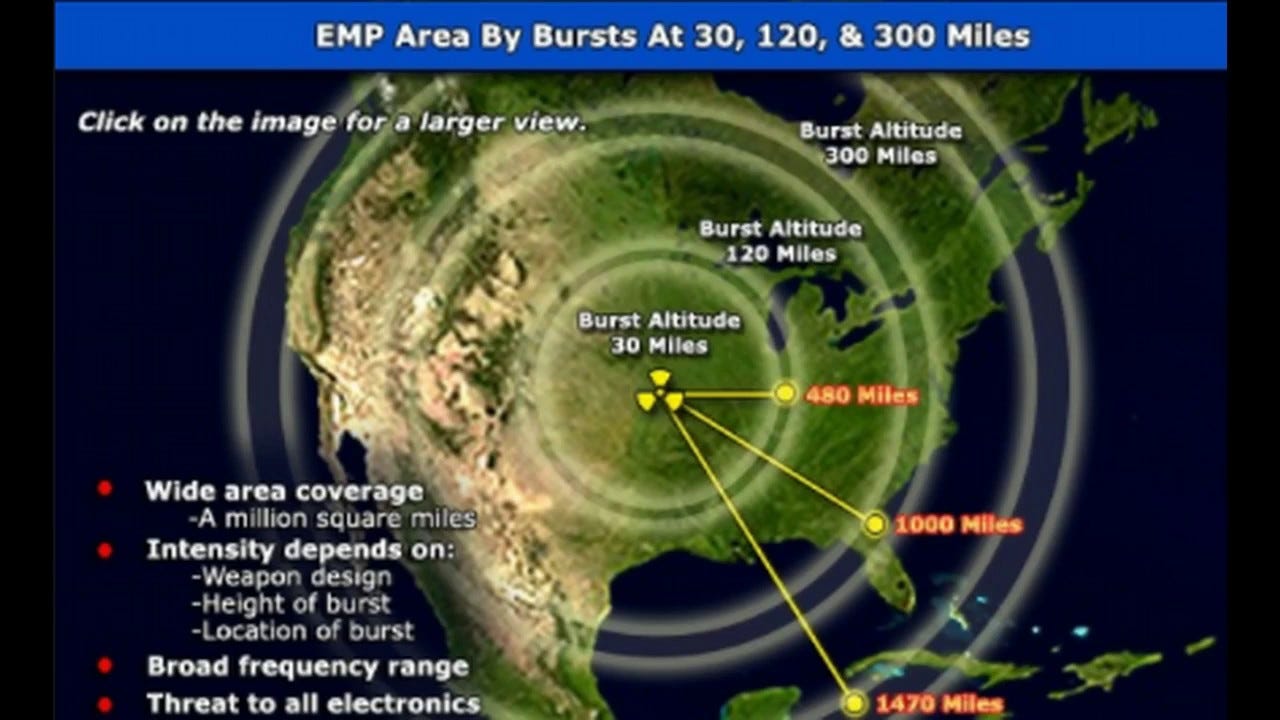
The phrase “electromagnetic attack” can refer to different things, but in this context most likely refers to a high-altitude electromagnetic pulse generated when a nuclear weapon is detonated in space, about 30 kilometers above the Earth’s surface. Once the weapon is detonated, an electromagnetic pulse can travel to the Earth’s surface and disrupt a wide variety of technology systems from appliances to a nation’s electric grid. Some characteristics of an electromagnetic pulse are similar to disturbances caused by solar flares.
There are also smaller electromagnetic pulse weapons that are being developed, but they would be unlikely to cause a power outage as large as the one Venezuela experienced, experts said.
The term electromagnetic attack also can refer cryptography, or an attack where the perpetrator is seeking secret keys or passwords, but that’s more likely to be directed at portable electronic devices, not electric grids, said Shucheng Yu, an associate professor of electrical & computer engineering at Stevens Institute of Technology.
HAS ELECTROMAGNETIC PULSE TECHONLOGY EVER BEEN USED?
In 1962, during the Cold War, the U.S. detonated a nuclear weapon above the atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean, and the experiment — known as Starfish Prime — knocked out power to traffic lights and telecommunications in parts of Honolulu, illuminating the sky and even leading hotels to host viewing parties, according to news reports.
Russia conducted a series of “high-altitude nuclear bursts” in 1961 and 1962 to test electromagnetic pulse impacts over Kazakhstan and destroyed that country’s electrical grid, according to testimony in front of Congress from the Commission to Assess the Threat to the United States from Electromagnetic Pulse Attack.
COULD VENEZUELA HAVE SUFFERED FROM AN ELECTROMAGNETIC ATTACK?
While several countries have capabilities to detonate a nuclear weapon and cause an electromagnetic pulse, it’s unlikely that such a maneuver would escape the world’s attention.
“If he’s suggesting that the U.S. detonated a nuclear weapon above the atmosphere, you think that would happen without anyone noticing? I don’t think so,” Burke said of Maduro’s claim. “You can’t secretly detonate a nuclear weapon.”
A senior U.S. administration official said Maduro is to blame for the latest blackout because his government has mismanaged the economy and is responsible for the destruction of his country’s infrastructure. The official was not authorized to respond to questions about the blackout and spoke only on condition of anonymity.
Unlike a cyberattack, which can be carried out by a hacker in a basement, generating an electromagnetic pulse requires a state-sponsored weapon.
“It’s hard to imagine that actor being incentivized to pull off and conduct such an attack. It would be pretty aggressive to do that,” said David Weinstein, chief security officer at Claroty, a security company that specializes in protecting infrastructure. “Also, the power fails easily in Venezuela anyway, so it’s almost like a waste of the capability.”
HOW MUCH OF A THREAT DOES AN ELECTROMAGNETIC PULSE ATTACK POSE?
It depends on who you ask. While the technology to launch an electromagnetic attack exists, and the impacts could cause widespread damage to electronics, some security experts believe the likelihood of such an attack is low and the threat is overstated.
“If they want to knock out the grid, I was trying to think of 12 ways to do it, this wouldn’t be high on the list,” said Bill Hogan, professor of global energy policy at Harvard University. “The (U.S.) system is run very conservatively, there’s a lot of redundancy, and you’d have to be pretty sophisticated to knock out a lot of it.”
Others are convinced that an electromagnetic attack could wipe out vast swaths of the U.S. power grid for prolonged periods, potentially killing most Americans.
The Electric Power Research Institute, a think tank funded primarily by utilities, found in an April study that an electromagnetic pulse could trigger regional service interruptions but would not likely trigger a nationwide grid failure in the U.S.
But the Commission to Assess the Threat to the United States from Electromagnetic Pulse Attack, which has been sounding the alarm on the possibility of this type of attack for years, said in 2017 Congressional testimony that a nuclear electromagnetic pulse attack would inflict massive widespread damage to the electric grid. An attack on the U.S., it warned, would inevitably lead to a widespread protracted blackout and thousands of electronic systems could be destroyed, risking millions of lives.
President Donald Trump called on the Secretary of Defense to conduct research to understand the effects of EMPs in an executive order in March and called on the Secretary of State to work with allies to boost resilience to potential impacts to EMPs.
“I think it’s a good thing that awareness has grown, and the potential risks and consequences have captured people’s attention, but at the same time, the much more practical and frankly the threat that we’re facing on a day-to-day basis is the cyber threat,” Weinstein said.
What Does An Electromagnetic Pulse Do To The Human Body?
The nerves in our body are surrounded by sodium and potassium ions. The electrochemical action of ions interacting through the membrane of nerves causes neurons to release chemicals that affect other neurons and cause the body to respond. The movement of neuron action is electrically-caused by chemical interaction.
An electrical charge is involved but the signals between neurons are passed chemically, not as electrical current. As such the signals travel at less than 100 m/s (meters per second). Electric current in a wire travels at about the speed of light—186,282 miles per second (299,792,458 m/s).
Some research suggests that strong EMP may have a substantial effect on the cognitive processes of the left hemisphere of the brain. This research suggests that it can temporarily short-circuit the logical circuitry.
The conclusion was that magnetism can affect human metabolism at very high EMP levels. Fortunately, we are not exposed to such a high EMP threat.
HOW MUCH EMP CAN THE HUMAN BODY HANDLE?
One researcher stressed that since humans are not very conductive, the resistance inside our body limits how currents can change. Thus, mutual inductance is not an issue. The chemical ion gradient creates a charge difference between the inside and outside of nerve cells with a specific voltage across a typical neuron measured at -70mV.
Mutual Inductance Definition:
This is the measure of the production of energy produced in one circuit based on the changes in the current of another circuit.
Our bodies can withstand a 100 kV/m EMP spike from a nuclear bomb so it takes a much larger spike to cause a noticeable effect on the body.
One engineer described experiments with EMP of 25kV with no effect on the staff involved. While several neuroscientists stated that humans can easily withstand EMP up to 100kV/m without detrimental effect.
A small nuclear weapon generates 100kV/m so even the EMP from such a terrorist nuclear detonation shouldn’t hurt you. However, your electronics can indeed be damaged–which calls for the use of EMP protection.
Some people claim that EMP can short out a pacemaker, but I found no report of actual pacemaker failure directly attributable to it.
ARE THERE OTHER SOURCES OF EMP?
People near earthquakes can sometimes feel anxious, uneasy, disoriented, and physically sick, but scientists think these feelings are caused by low-frequency sound (infrasound) or electromagnetic fields produced during the movement of the earth—not from a pulse of EMP.
Radar and microwave radiation can cook flesh so should be avoided. Time-varying magnetic fields can also affect the human body.
A 14-watt TASER stun gun can cause muscle contraction and 26-watt electromagnetic discharge EMD weapons can override the central nervous system and affect all the muscles in the body, but these devices won’t kill you.
A short pulse EMP should pass through the body with no effect. The conditions are simply not present in an EMP from a solar flare, nuclear detonation, or electromagnetic weapon to produce damage to the body. Just don’t let the gamma rays or explosion shock wave get to you.
IS EMP FATAL FOR HUMANS?
The key to EMP and damage to the body is the duration of the pulse. A quick pulse would pass right through. Making an EMP attack probability to be unlikely to happen.
To cause damage would require a sustained magnetic field that is constantly increasing in magnitude, thus causing current flow for at least a few milliseconds. But then, this would no longer be a pulse.
Government technical threat assessments conclude that EMP passes through you so fast, current cannot begin flowing in your body to cause harm. And I concur.
So don’t be worried that EMP can harm you. Your body should be fine. Instead, focus on protecting your electrical and electronic systems.
The post Could America survive an electromagnetic attack (EMP)? appeared first on Movie TV Tech Geeks News By: Jeffrey Lang